Savanthi Murthy
USER EXPERIENCE RESEARCHER
Can a piece of furniture be inexpensive, easy to assemble/disassemble, eco-friendly, strong and elegant at the same time?
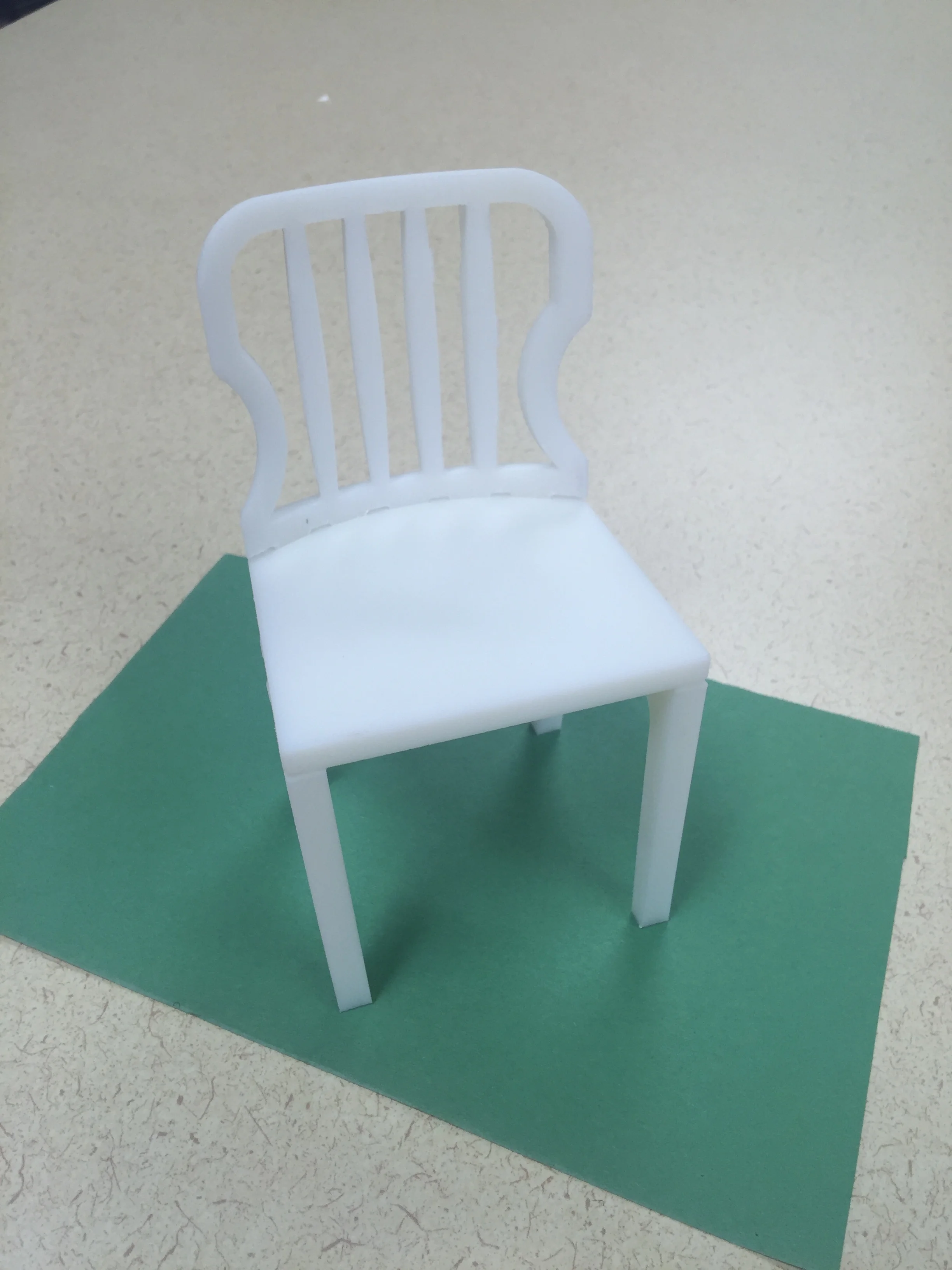
White. is an innovative chair concept that which eliminates the need for fasteners by using dovetail joints and parts that fit into each other. It also minimizes the pain of assembly, disassembly and transport. The chair explores the use of a new material for furniture while facilitating easy manufacturing processes and low costs.
Team Project
My Role
Technical Lead , Design of structure and assembly based on DFMA principles
Ergonomic considerations and Aesthetics
Material & manufacturing process selection
Creation of CAD model & 3D printed model, Stress analysis
What is the problem with existing flat-pack furniture?
Many instructions that accompany flat-pack furniture are difficult to understand and appear like optical illusions.
At one end of the spectrum, some furniture brands produce furniture at an accessible price point. However, these products are not intended for disassembly, transport or reassembly. Instead, they are weak flat-pack assemblies with complex instructions.
The instructions are often complex and have many errors. This requires customers to seek assistance and pay for it.
At the other end of the spectrum, there are companies offering high-quality, well-designed furniture with variable assembly requirements at an exceptionally high cost.
Who will use this chair?
Persona:
Our customer is young. She might switch jobs 10 times in her career, and she loves meaningful experiences. She’s willing to move a lot- in fact, she almost expects it.
You might call her a “millennial.”
Her home is her nest. She watches movies, she frequently hosts small get-togethers and at this point maybe only the occasional party. She has close friends and enjoys sharing with them a home she has designed as an extension of herself. And while her identity is fluid, she is creative and values her time and the many things she can do with it. She wants to get things done in a cost-effective way- but she doesn’t want to compromise on quality.
For all of these reasons, when she buys furniture, she sees it as an investment. It is not something she plans to sell or throw out; it is a statement piece, and when she moves, she wants to keep it with her- she will want to keep it as long as she associates it with her identity.
The Challenge
Process
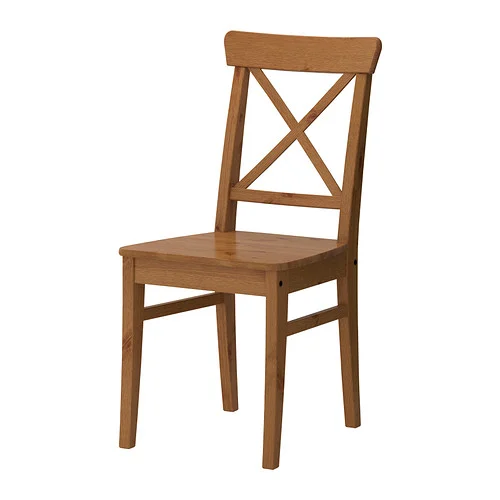
Initially, the team identified and bench-marked popular dining chairs from brands like Ikea, Knoll and others. This analysis included a bill of materials as well as assembly instructions. The 'Ingolf' chair from Ikea was identified as the product that our concept would be comparable to. This chair has 7 wooden parts, 22 fasteners and requires 2 tools to assemble, with 12 steps for assembly.
We found that the large number and variety of fasteners left the customers perplexed and unhappy. The list of instructions had too many steps and the assembly required the use of tools, which not all the customers would possess. This led to the idea of White., a simple dining chair which required no fasteners or tools for assembly and was just as easy to disassemble.
The concept of using dovetail joints was validated by the existing furniture and storage concepts .
Preliminary research and subsequent understanding of some of the common materials used for furniture helped narrow down our long list of potential material choices. ABS, glass-filled polypropylene, pine wood and wood-plastic composites were identified as the preferred materials for the chair. These were reduced to pine wood and PWC. There were three factors which led to the choice of wood plastic composites over pine wood:
“Wood/PP biocomposites
- Contain up to 50% organic fibers
- Can be injection molded.
- Are lower in cost and weight than unfilled resins or glass-filled resins.
- Can be dyed with excellent results.
- Have the advantage of Lower density.
- Have combined properties of wood and plastic
- Have good moisture barrier, can be screwed or nailed like wood, along with an organic look and feel.
- Parts can be made with thick walls would benefit from excellent rigidity and dimensional stability.”
- The time, effort and level of detail and craftsmanship required each time to manufacture the wooden version is higher compared to the composite version.
- While pine wood can be obtained from Sustainable Forestry Initiative approved sources, using the composite would be more eco-friendly as it uses recycled wood and can be recycled at the end of its life.
- Wood plastic composite can be manufactured using injection molding. This would have high initial tooling costs, but operating costs would be significantly lower and level of precision would be higher.
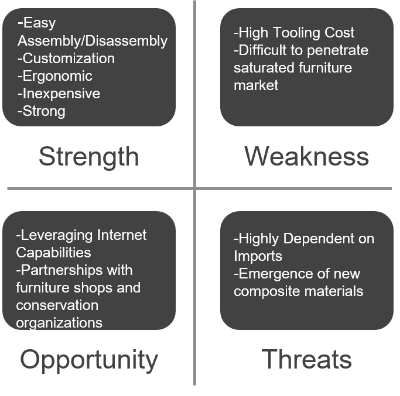
A preliminary cost analysis indicated that White. can be manufactured at low costs as the cost of the material and injection molding are reasonable. These can offset the high initial tooling costs. A SWOT analysis helped us understand the opportunities and threats associated with the concept.
Prototype
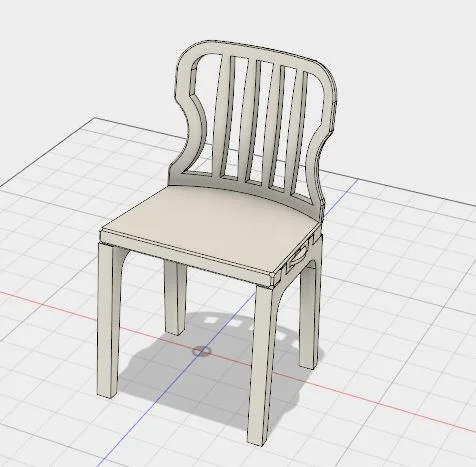
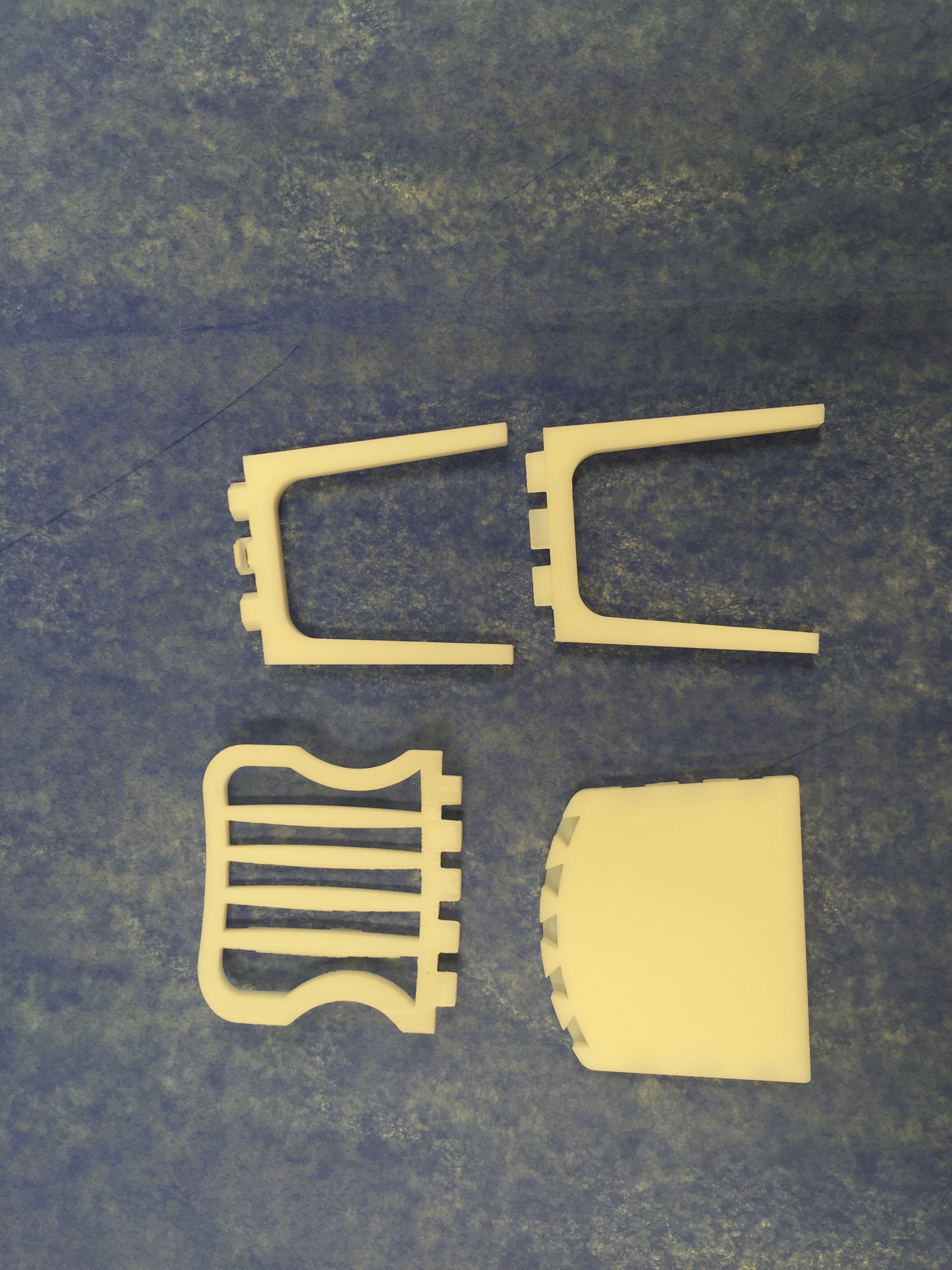
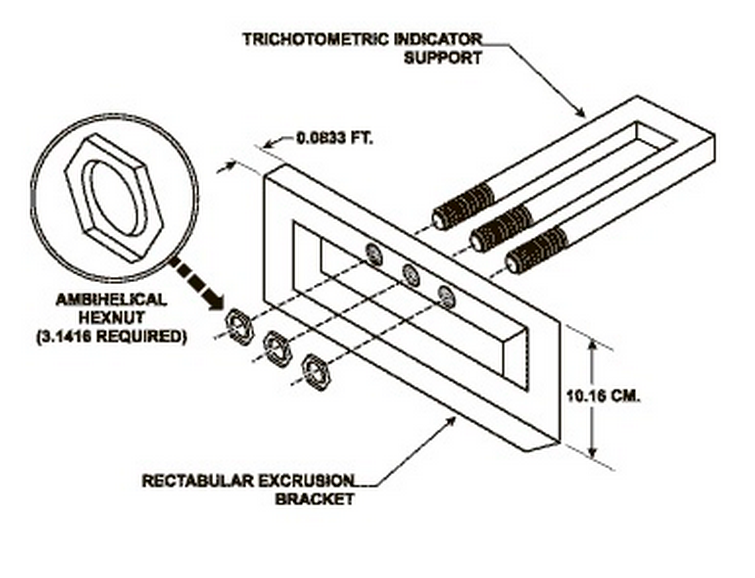
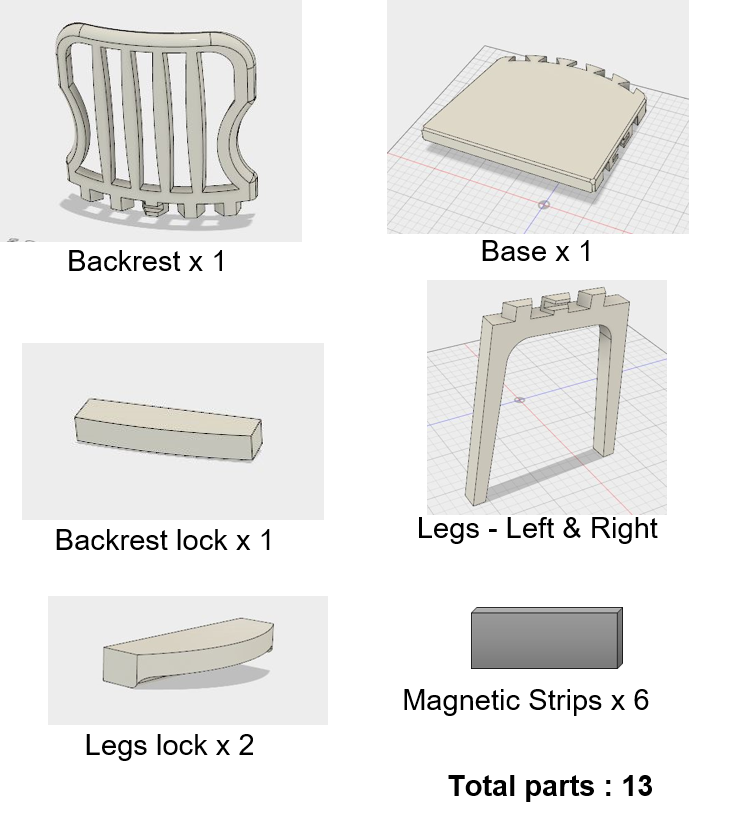
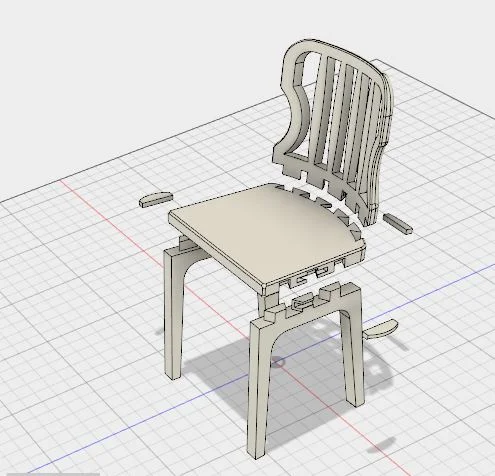
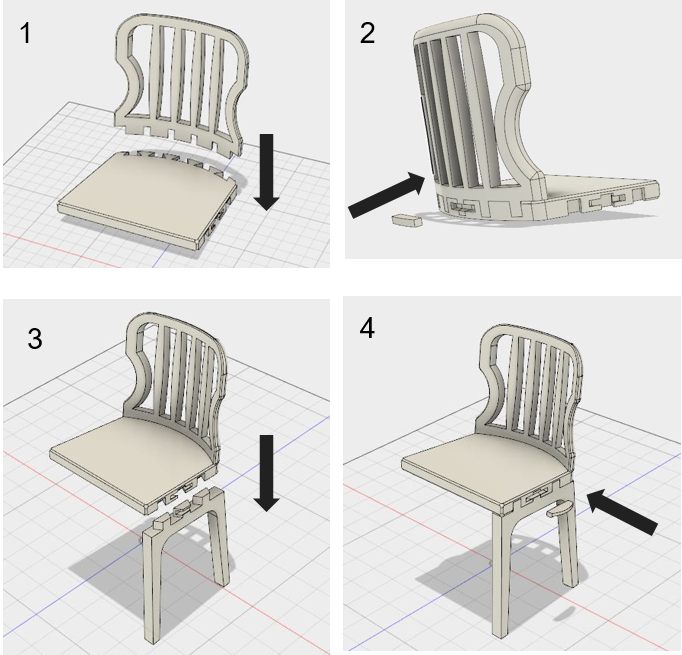
Digital Prototype: The digital prototype was created on Fusion 360. The assembly consists of only 7 parts and is intuitive. Magnetic lock pieces are provided to constrain all the degrees of freedom, particularly disassembly in the direction of assembly. Magnetic strip rolls are inexpensive and will be pre-assembled by gluing on to the mating parts. The user need not glue them on.
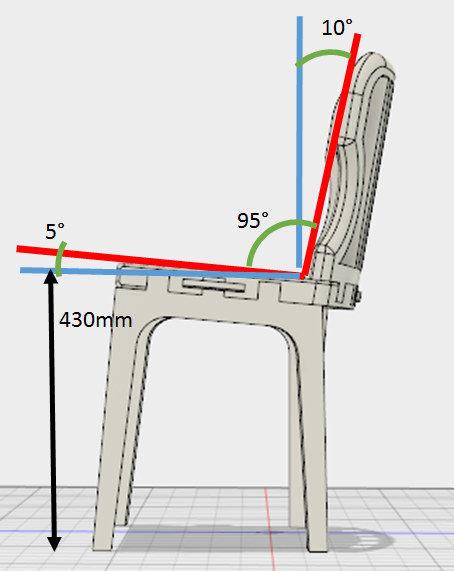
Ergonomic principles of dining chairs were studied, understood and implemented in the design. The assembly sequence was made intuitive and simple.
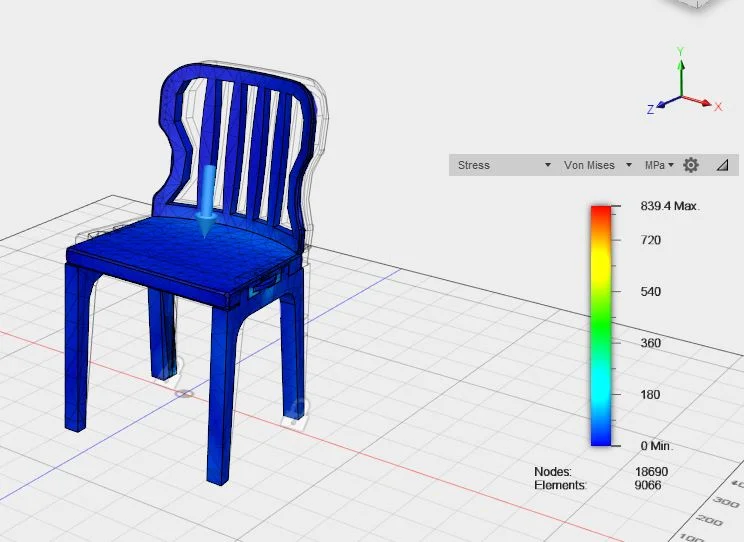
A stress, strain and displacement analysis was performed on the structure using a material with similar properties on Fusion. A static force of 1500N was applied on the sitting area/base of the chair.
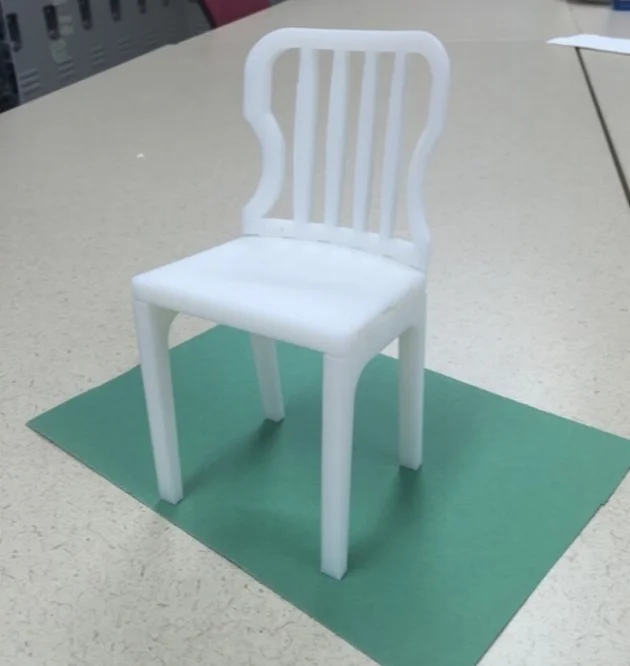
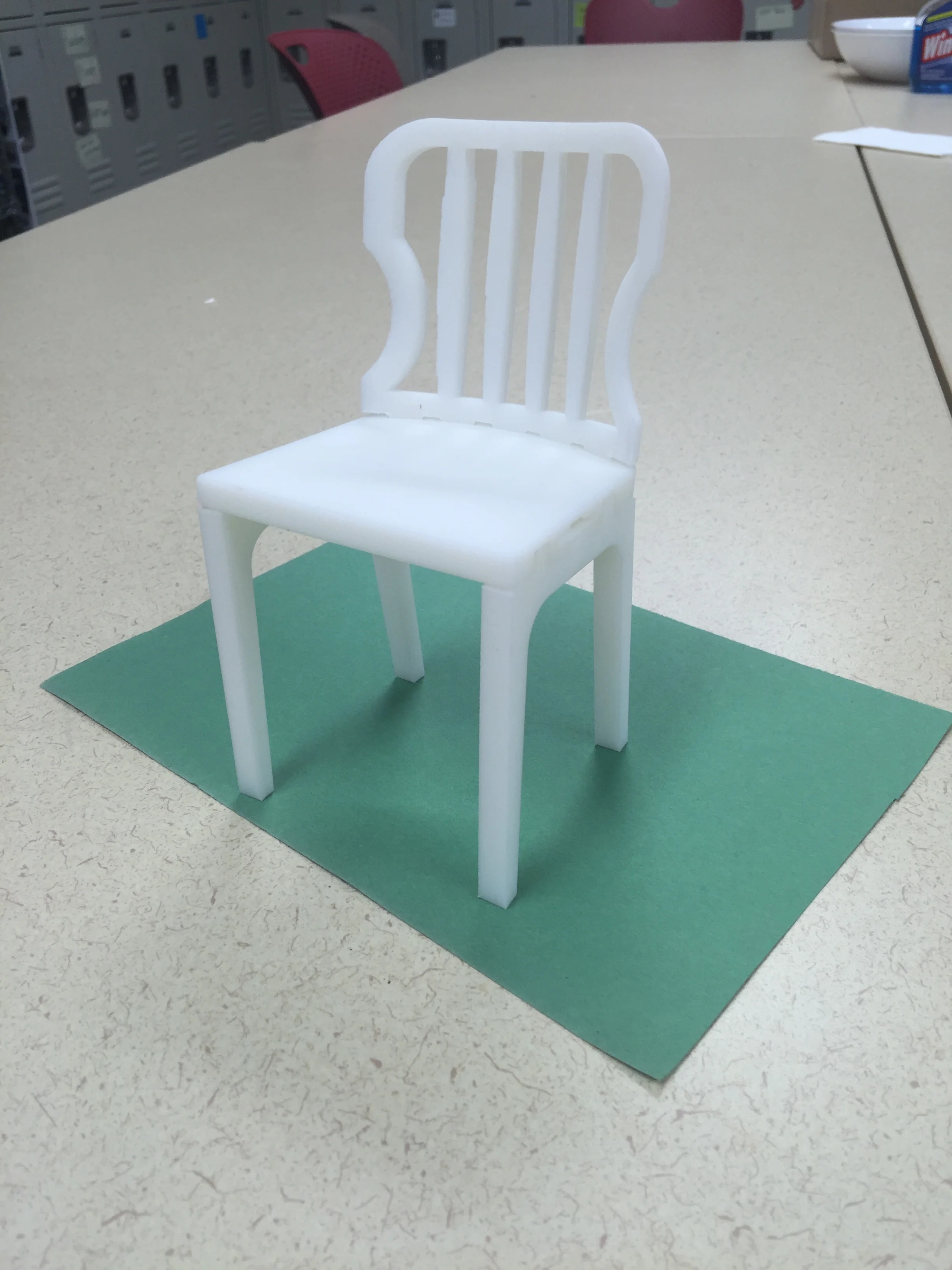
The virtual prototype was then 3D printed to validate the concept.
Result
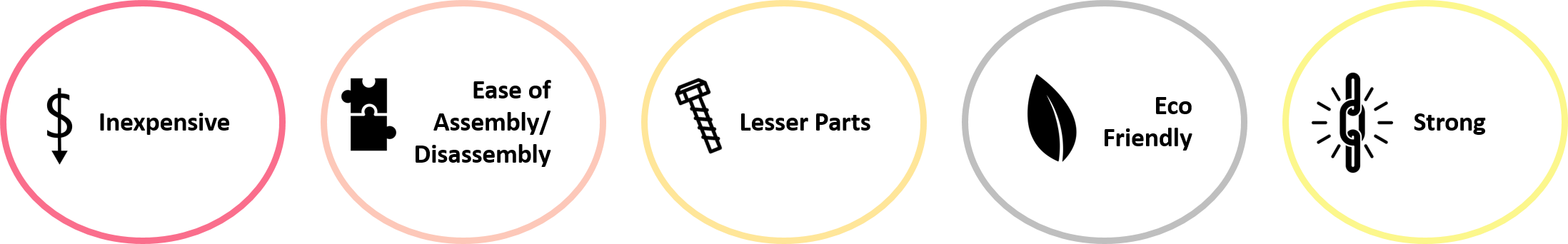
- White. reduced the number of parts for a dining chair from 29 to 13 and number of assembly steps from 12 to 5.
- It is as easy to disassemble as it is to assemble.
- White. is eco-friendly, it uses recycled material with up to 50% organic content and can be recycled again at the end of its life.
- It is strong and can withstand heavy loads.
- It is fairly inexpensive as the high initial tooling cost can be offset by low cost of material and low operating costs.